Introduction:
Individuals and organizations continue to be threatened by malware in an ever-evolving digital geography. As a cybersecurity firm, it is crucial to educate our audience on the complications of malware, its various forms, and how to safeguard against it. This comprehensive blog delves into the world of malware, highlighting its impact and offering essential protection strategies. Let’s delve into the world of malware using the 5W and 1H approach:
Who Creates Malware?
Malware can be created by a wide range of individuals, from lone hackers to organized cybercrime syndicates. It can target anyone using digital devices, from individuals to large corporations. Cybercriminals and hackers often deploy malware to exploit vulnerabilities, steal sensitive data, or disrupt operation.
What is Malware?
Malware (malicious software) refers to any software intentionally designed to cause damage to a computer, server, client, or computer network. Using malware, cybercriminals can steal sensitive information, disrupt business operations, and gain access to systems without the owner’s permission. The term encompasses various types of harmful software, each with unique characteristics and purposes.
When Does Malware Strike?
Malware attacks can occur at any time, often exploiting vulnerabilities in software or operating systems. However, they often spike during periods of heightened online activity, such as holidays or major events, when users might be less vigilant about cybersecurity. Staying informed about the latest threats is essential for proactive protection.
Where Does Malware Hide?
Malware can infiltrate systems through various channels, including email attachments, malicious websites, infected software downloads, and removable media. Cybercriminals employ increasingly sophisticated methods to conceal malware, making detection and removal challenging. Essentially, any connected device is at risk.
Why Do People Create Malware?
The motivations behind malware attacks vary widely. Common reasons include financial gain through stealing sensitive information for resale or ransom demands from victims. Other motives include corporate espionage, political activism (hacktivism), cyberterrorism or simply causing disruption and reputational damage.
How does Malware Spread?
Malware can infiltrate systems through various vectors. Understanding these methods can help in implementing effective defenses:
- Phishing Emails:
Cybercriminals send deceptive emails that trick users into clicking malicious links or downloading infected attachments. - Malicious Websites:
Malware can be downloaded automatically by visiting a compromised or malicious website. - Software Downloads:
Downloading software from untrusted sources can result in inadvertently installing malware. - USB Drives:
Infected USB drives can spread malware when connected to a computer. - Network Vulnerabilities:
Exploiting weaknesses in network security allows malware to spread across connected devices.
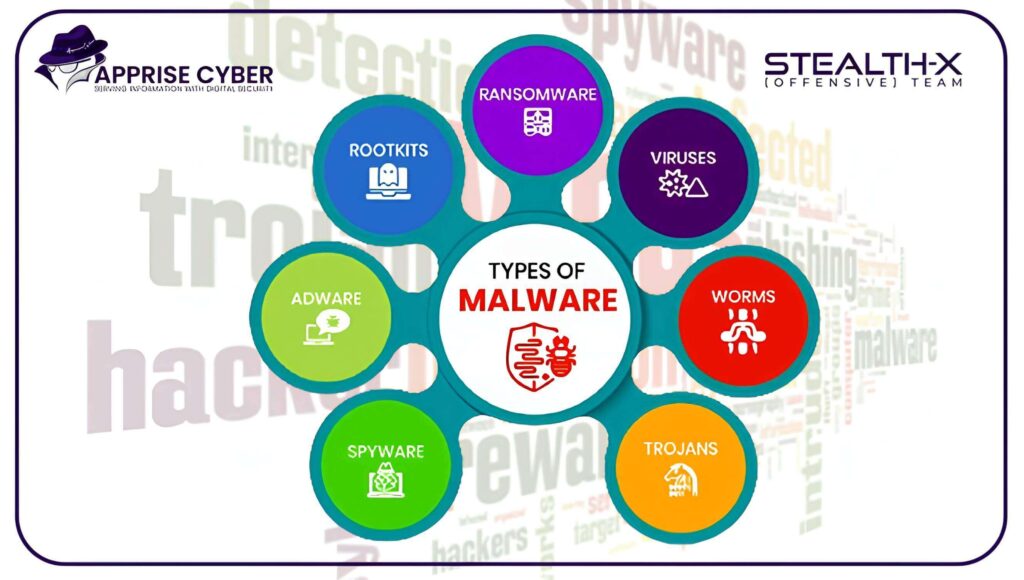
Types of Malware
Understanding the different types of malware is the first step in combating them. Here are the most common types:
- Worms:
A worm is a piece of standalone malware that replicates itself in order to spread from one computer to another. Unlike viruses, they do not need to attach themselves to a host file and often exploit network vulnerabilities. - Trojans:
In order to trick users into installing them, Trojans disguise themselves as legitimate software or files. Once installed, they can create backdoors to give cybercriminals access to the infected system. - Ransomware:
In ransomware, files are encrypted, and the victim is asked to pay a ransom for the decryption key. This type of malware has gained notoriety for targeting businesses and critical infrastructure. - Spyware:
Spyware secretly monitors user activity, collecting sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, and browsing habits. It often operates without the user’s knowledge, leading to significant privacy breaches. - Adware: Adware often redirected users to malicious websites by showing them unwanted advertisements on their devices. Even though it isn’t always harmful, but it can have an adverse effect on the user experience and the performance of the system.
- Rootkits:
Rootkits provide remote access and control over a computer, often hiding their presence and other malicious activities. They are challenging to detect and remove due to their ability to operate at a low system level.
The Impact of Malware Attacks
The consequences of a malware attack can be devastating for individuals and organizations:
- Data Breaches:
A malware infection has the potential to put sensitive data at risk, leading to financial losses and harm to an individual’s reputation. - Operational Disruption:
Ransomware and other destructive malware can halt business operations, leading to significant downtime and financial loss. - Financial Loss:
Costs associated with ransomware payments, data recovery, and system restoration can be substantial. - Legal Consequences:
Data breaches can result in legal actions and regulatory fines, especially with stringent data protection laws in place.
Protecting Against Malware
Effective protection against malware involves a multi-layered approach. Here are essential strategies:
- Regular Software Updates:
Ensuring your software and operating systems are regularly updated helps fixing known security weaknesses. - Use of Antivirus Software:
Reliable antivirus software can detect and remove known malware, providing a critical layer of defense. - Firewalls:
Firewalls act as barriers between trusted and untrusted networks, preventing unauthorized access. - Email Filtering:
Implementing email filtering solutions can block phishing emails and other malicious communications. - User Education:
Educating users on safe browsing habits, recognizing phishing attempts, and the importance of not downloading untrusted software is crucial. - Regular Backups:
Regularly backing up data ensures that it can be restored in the event of a ransomware attack or data corruption. - Network Security:
Implementing robust network security measures, such as intrusion detection systems and network segmentation, can limit the spread of malware.
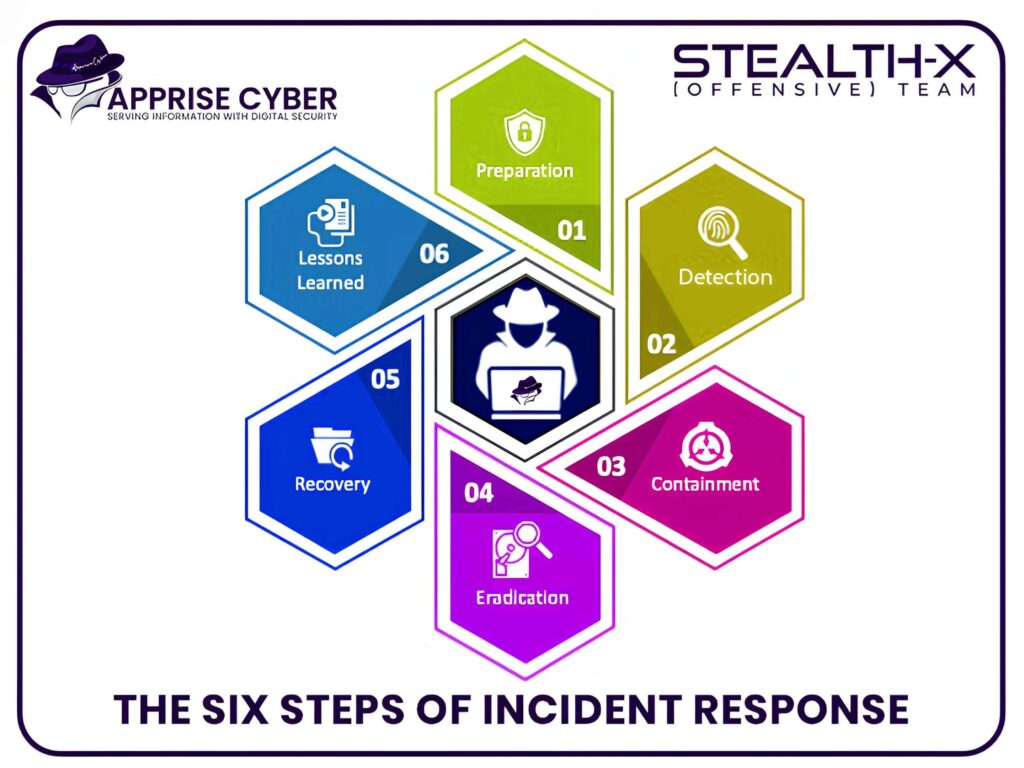
Incident Response Plan
Having a well-defined incident response plan is essential for quickly addressing and mitigating the effects of a malware attack:
Preparation:
Developing a detailed and effective roadmap to quickly address and mitigate security incidents.
Detection and Analysis:
Identifying the presence of malware and understanding its scope and impact.
Containment:
Isolating infected systems to prevent further spread of the malware.
Eradication:
Removing the malware from all affected systems.
Recovery:
Restoring systems and data to normal operation, ensuring no traces of the malware remain.
Post-Incident Review:
Analyzing the incident to improve future defenses and prevent recurrence.
Conclusion
In the digital age, where attacks grow as people starts working remotely, malware remains a pervasive threat that can cause significant harm to individuals and organizations. By understanding the various types of malware, their methods of spreading, and implementing robust protection strategies, we can mitigate the risks and safeguard our digital assets. Regular updates, comprehensive security measures, user education, and an effective incident response plan are vital components of a strong defense against malware.
Stay informed, stay vigilant, and prioritize cyber security to protect your organization from the ever-present threat of malware.
Call to Action
Protect your business from malware threats by partnering with the experts of our cybersecurity firm. Stay updated on the latest cybersecurity threats and safeguard your digital assets with expert tips and solutions.
Get in touch with us now to discover in-depth details regarding our extensive security offerings and the ways in which we can protect your valuable digital assets.
By implementing these strategies and staying informed about the latest threats, you can significantly reduce the risk of malware attacks and protect your valuable data and systems. Make sure to prioritize your safety and security in the digital world!